From Empirical Problem-Solving to Theoretical Problem-Finding Perspectives on the Cognitive Sciences
Abstract
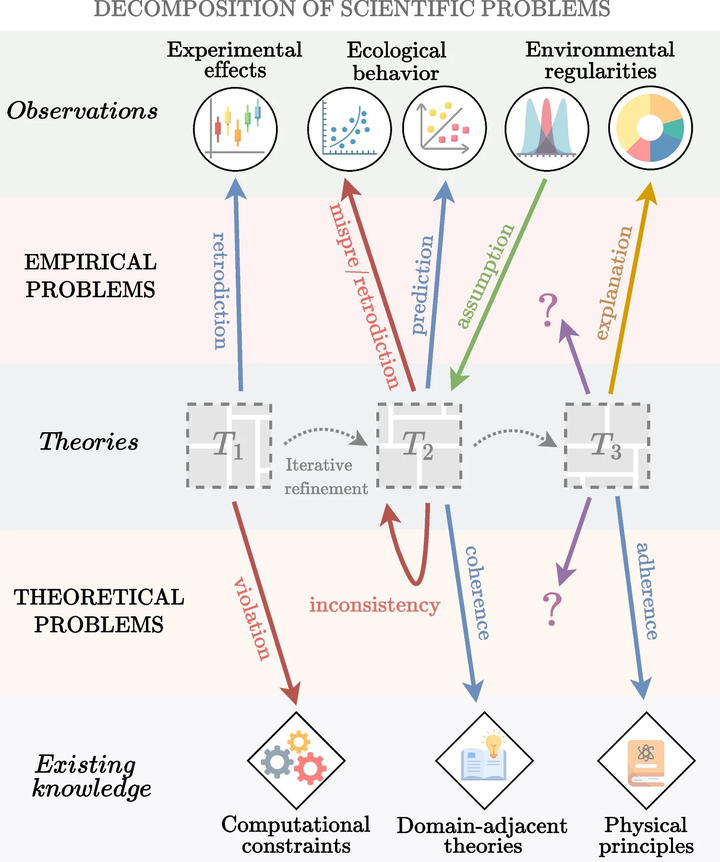
Meta-theoretical perspectives on the research problems and activities of (cognitive) scientists often emphasize empirical problems and problem-solving as the main aspects that account for scientific progress. While certainly useful to shed light on issues of theory-observation relationships, these conceptual analyses typically begin when empirical problems are already there for researchers to solve. As a result, the role of theoretical problems and problem-finding remain comparatively obscure. How do the scientific problems of Cognitive Science arise, and what do they comprise, empirically and theoretically? Here, we attempt to understand the research activities that lead to adequate explanations through a broader conception of the problems researchers must attend to and how they come about. To this end, we bring theoretical problems and problem-finding out of obscurity to paint a more integrative picture of how these complement empirical problems and problem-solving to advance cognitive science.